Select a platform to begin your company's trucking licensing.
Packages offer content, tools, development, and support for your trucking career, regardless of experience.


Arbitration Program
Required for Household Goods Carries

Start a Trucking Company
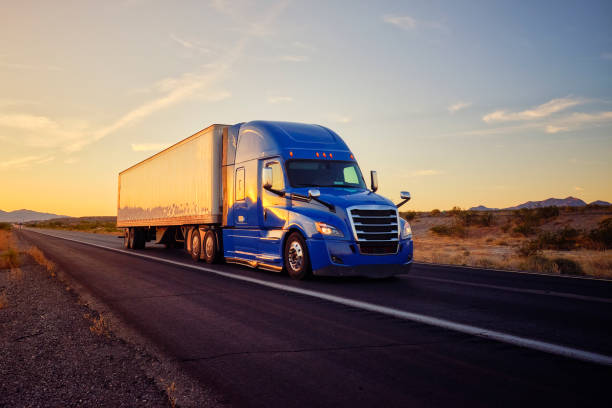
Trucking business can be very profitable.

Trucking Authority Packages
Interstate Authority Packages. FMCSA Administration registration done correctly & Quickly.

UCR Registration
Get everything you need to operate.
MC number
Required to cross state lines

Improvement Package
Interstate Authority Packages. FMCSA Administration registration done correctly & Quickly.

New Jersey Tariff
Custom Tariff with all New Jersey required contracts included.

Broker Freight Package
Begin the process of Obtaining an USDOT Number.

Motor Carrier Authority
Get everything you need to operate.

USDOT Number
USDOT numbers must be displayed on your motor carrier vehicle.
Military Moving Authority
Interstate Authority Packages. FMCSA Administration registration

BOC 3 Filing
Required bi-annual filing

Carrier Agreement
Required legal documents for carriers.

Interstate Tariff
Custom company Tariff with all required Contracts included.

Claims Package
Trucking business can be very profitable.

Biennial Update
Custom company Tariff with all required Contracts included.

CA Number $289
In California you must have CA dot to Operate

The Double Drive Time Law
the (CPUC). According to these laws, customers can only be charged certain costs during an

Intrastate Moving Companies California
to learn about key intrastate details that can help your California moving company succeed.

BOC-3 101, Do I need a BOC-3 for intrastate business?
file: the BOC-3.
BOC-3: How To Choose The Right Process Agent. This
Moving Companies in the USA
To find a specific moving company, enter the company’s
name or DOT Number below.